Secure SDLC

To help you in your security journey, there are several tests and other actions that can be performed at different stages of the software lifecycle. For an idea of how and when certain tests and actions are performed, take a look at the following secure SDLC:
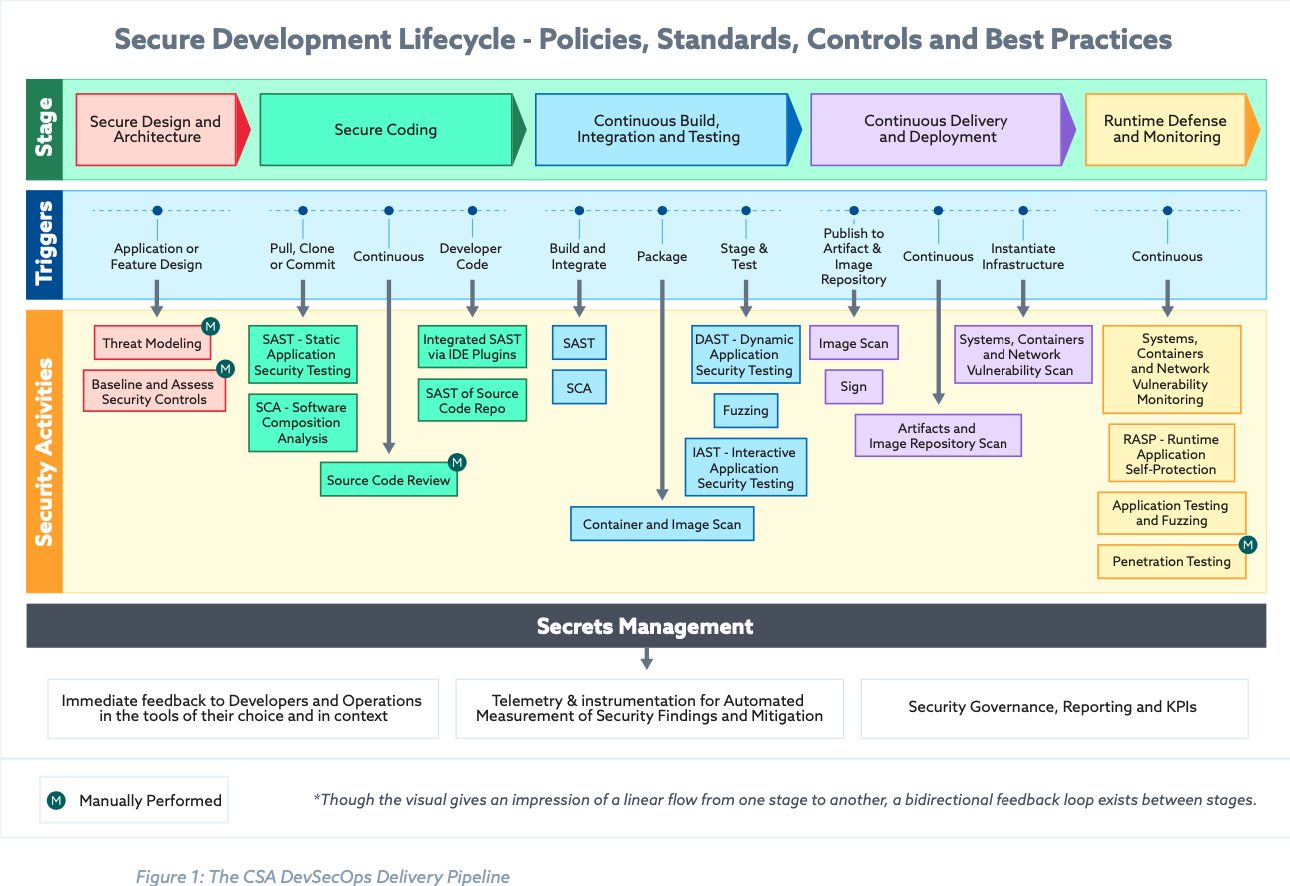 Figure from Six Pillars of DevSecOps: Automation by the Cloud Security Alliance
Figure from Six Pillars of DevSecOps: Automation by the Cloud Security Alliance
Threat modeling and security assessments were covered in the Shift Left section of this guide, but what about the rest? For the breakdown, you’ll see each action is preceded by a trigger. For example, the static testing is not done at any point in the secure coding phase, but specifically should be done whenever there are changes to the codebase. As for the actions themselves, here’s a quick overview separated by stage. (For tests that are repeated in more than one stage, they are listed under the first stage they appear.)
Secure Coding#
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- SAST, also referred to as Static Code Analysis, does not require a compiled application to run - so it can, and should, be run early in the SDLC. The test reveals vulnerabilities in the code, specifically those in the OWASP Top 10 like SQL injection.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
- A software composition analysis scans software, as well as its dependencies, and displays a list of known vulnerabilities as well as licenses and noting any deprecated dependencies.
- Secure Code Review
- “A secure code review is a specialized task involving manual and/or automated review of an application's source code in an attempt to identify security-related weaknesses (flaws) in the code. It does not attempt to identify every issue in the code, but instead looks to provide insight into what types of security-related problems exist and help the application developer understand what classes of issues are present.” (Mitre)
Continuous Build, Integration, and Testing#
- Container and Image Scan
- Checks the build process of your containers and images for vulnerabilities. This should be done to establish trust with the base image or container, as well as any composites.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- DAST is for compiled code / a running application without knowledge of the environment, simulating a hacker. Since the code is running for the test, this test is good for identifying issues with the runtime environment as well. Note that DASTs are only run on web applications and services.
- Fuzzing
- Testing with unexpected inputs. This can be something like testing if a non-date is entered in a date field, or even (trying to) drop a binary file in a text field. The goal is to capture these cases and ensure that the application does not crash and gives a usable error message.
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
- An IAST tests the running application for vulnerabilities during use, similar to a DAST. Unlike a DAST, an IAST can identify the line of code that is the source of a particular vulnerability.
Continuous Delivery and Deployment#
- Sign
- Verifies both the signature of the code and that the code has not been tampered with. This can be done for local and/or remote signatures and uses a cryptographic hash.
- Artifacts and Image Repository Scan
- An artifact scan scans all the artifacts that were created during development for vulnerabilities, and an image repository scan scans images when they are pushed to a repository. Any images that fail the scan are not uploaded.
- Systems, Containers, and Network Vulnerability Scan
- Scans for known vulnerabilities in the systems, containers, and networks.
Runtime Defense and Monitoring#
- Systems, Containers, and Network Vulnerability Monitoring
- Monitoring systems, containers, and networks for known vulnerabilities with observability tools.
- Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
- Briefly, RASP works by adding sensors into the code so that execution points to watch for exploits happening in real time.
- Penetration Testing
- Penetration testing, frequently referred to as pen testing, is a simulated attack to test for vulnerabilities. This type of testing can be done either black box or white box and can be done on the applications, services, systems, networks, etc.
